One of the most important and confusing topics in OSPF is the LSA types, so it’s important for us to learn it because it can help us in troubleshooting OSPF. Since its a big topic, let’s break this down into two parts and let’s look at LSAs 1-5 first with configuration examples.
LSA Type 1 – Router LSA
Every router within an area will generate a Type-1 LSA, all the directly connected links will be shown in this LSA.
LSA Type 2 – Network LSA
This type is LSA is created for multi-access network like the broadcast or non-broadcast, this type of LSA is generated by the DR and we will find all the routers connected to the multi-access network.
LSA Type 3 – Summary LSA (not to be confused with network summarization)
Also known as the Inter-Area LSA is generated by the ABR and it advertises the summary LSAs from one area to another connected area.
LSA Type 4 – ASBR Summary LSA
Type 4 LSA is generated by the ABR, it informs it’s areas about how to reach ASBR (autonomous System Border Router) and it includes the ASBR’s Router-ID.
LSA Type 5 – ASBR External LSA
The ASBR generated Type 5 LSA to advertise external redistributed routes, these routes are flooded throughout the whole OSPF domain.
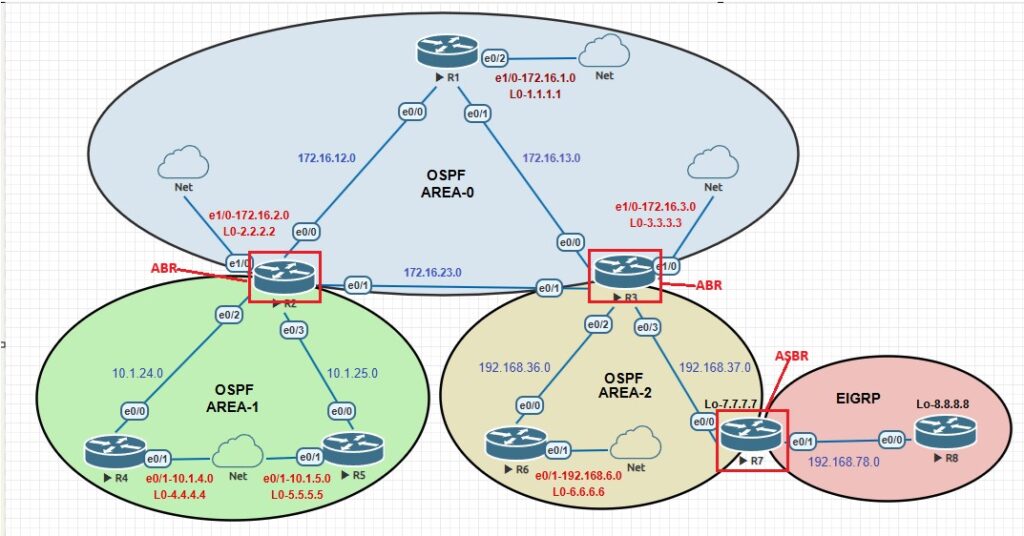
Let’s take a look at the LSAs in regards to our topology
LSA Type-1 – Router LSA
looking at the topology we can tell that R1 LSA type-1 will tell us about all the directly connected networks/links.
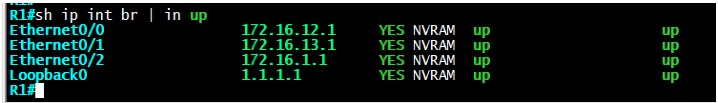
First we will take a look at R1 interfaces, we can see that it has 4 interfaces.
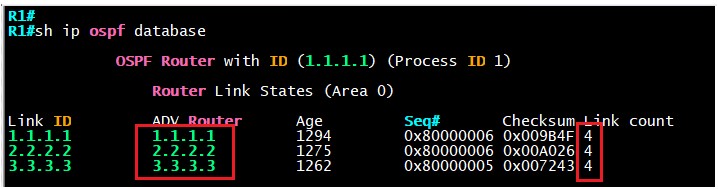
If we run the sh ip ospf database command it will tell us about the router LSA for R1, let’s take a look.
All 3 routers show the same number of interfaces, we can go into more details about R1 router LSA.
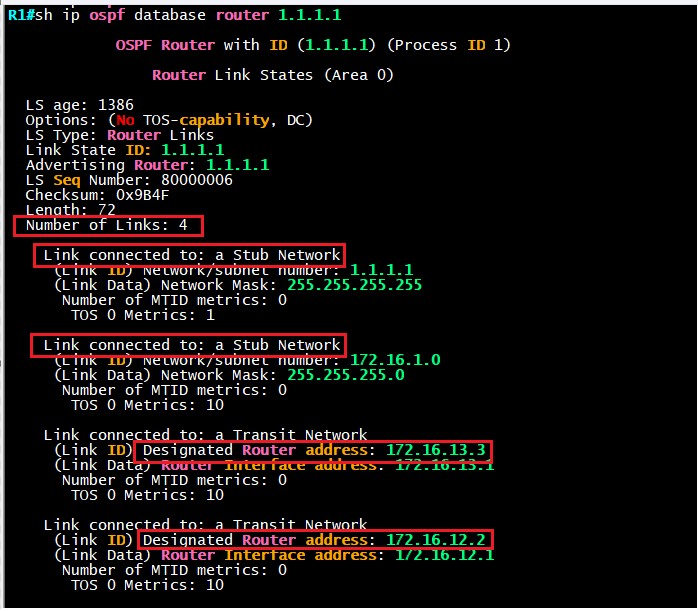
We can see all the 4 directly connected networks that R1 is connected to, it’s also showing the 2 stub networks, loopback and int e0/2. We also see the DRs for the two different segments.
This is Type-1 Router LSA, which shows R1 networks that it’s currently connected to. Each area will have it’s own Router LSAs. Type-1 LSA do not propagate between different areas, the type-1 LSAs for area 0 will not know any information about area 1 or area 2 Type-1 LSAs and vice versa.
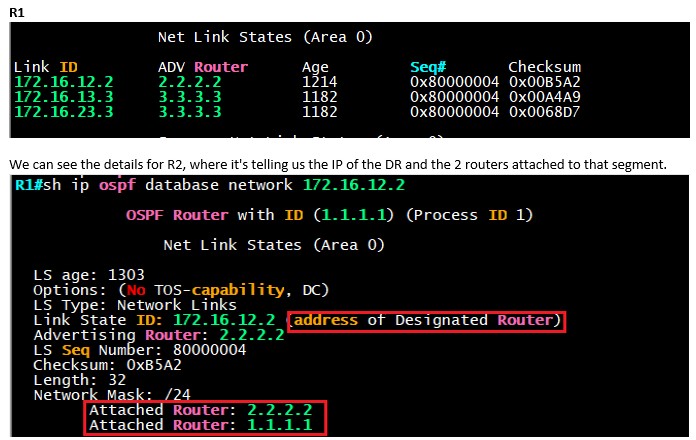
LSA Type-2 – Network (Interface IP of DR)
The designated router advertises this LSA on behalf of a network they’re connected to where they are the DR.
In our topology if we run the “sh ip ospf database” command we see that 172.16.12.2 is R2 and it happens to be the DR for the 172.16.12.0 segment and we see the other 2 routers as well who are the DRs for their respective segments.
LSA Type-3 – Summary (not network summarization)
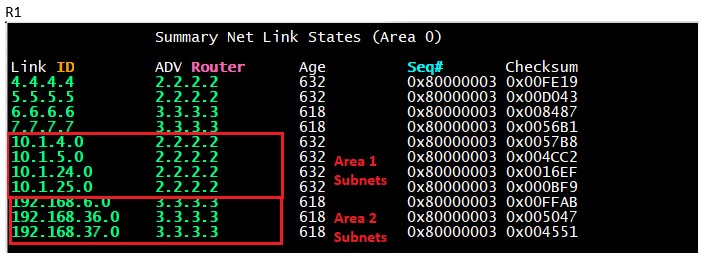
This type of LSA is generated by the ABR and in our topology the type-3 will be generated by R2 and R3.
R2 will generated type-3 LSA and it will advertise all the networks from area 1 and put them in the backbone area (area 0) and R3 will advertise all the networks from area 2 and put them in backbone area (area 0).
We can take a look at the OSPF database of R1 to verify-
We can see the routes from Area 1 and Area 2 being seen in the Area 0 LSDB.
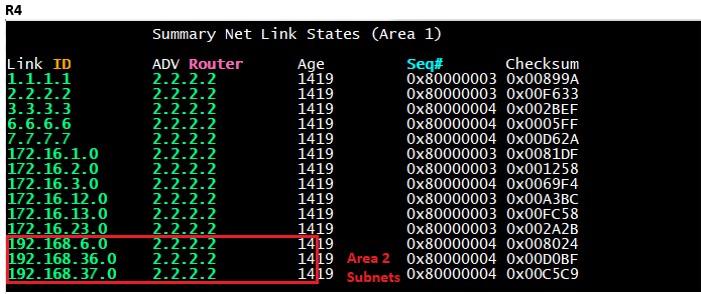
We can also see the OSPF database of R4 and see all networks from area 2 being added to area 0 and then R3 will make them available to area 1.
This is how all the routers will know about all the different networks in all the areas, hence the name network LSA.
LSA Type-4 – ASBR Summary (Router ID of ASBR)
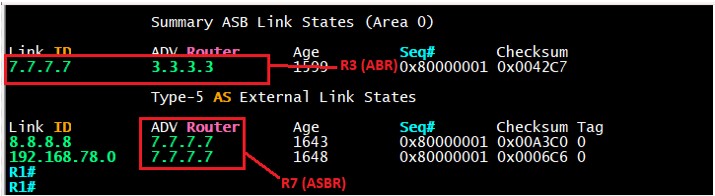
LSA type-4 is a bit confusing so let’s break this down, in short the Type-4 LSA is advertised by the ABR to let the routers know how to reach the ASBR. Let’s take a look at our topology, in this case our ASBR is R7 and the ABR connected to R7 is R3. R1 does not know how to reach R7 unless is advertised by R3. Let’s take a look at LSDB of R1.
Let’s look at R1 LSDB, in order for R1 to reach R8 (external network), it has to go through R7 so R3 is letting R1 know how to get to R7 which we see in the below image. This is LSA type-4 and it’s generated by R3 to let all the routers know of the Router-ID of R7.
LSA Type-5 – AS External
This type is LSA is generated by the ASBR and it shows the external routes that are injected or redistributed from another routing protocol into OSPF network.
In our topology the ASBR is R7 and it generated the Type-5 LSA (External) to let our OSPF network know about the redistributed network from EIGRP.
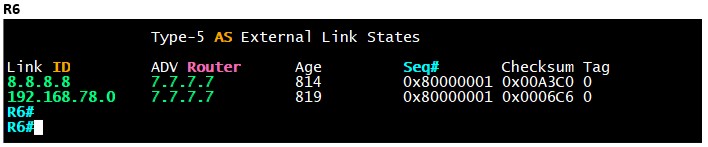
To verify that other routers have received the Type-5 LSA, we can take a look at the LSDB of R6.
We see the external EIGRP network in the LSDB of R6.
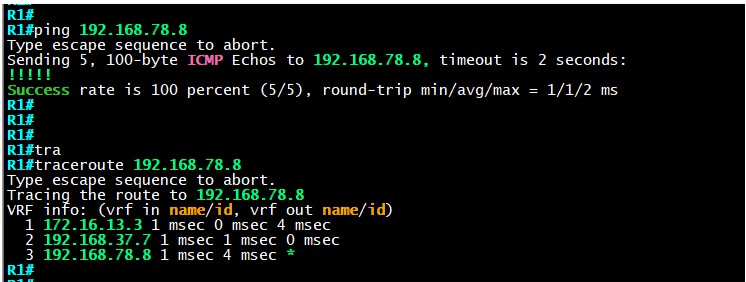
Now that we have a fully converged network, we can verify the connectivity from Area-1 to R8 which is our external network.
Hope this helps – Spin up a lab and try this out.